Intro
이번 글에서는 Compose의 Layout에 대한 정리와 대표적인 Custom Layout 사용방법에 대해 정리한다.

Composable함수는 Composer를 통해 Composition이 진행된다. 이때 ElementTree(contained CompositionData)가 생성되며 이를 통해 Layout → Drawing 과정을 거쳐 UI Rendering이 이뤄진다.
Compose는 Kotlin-Multiplatform Base로 구현되며 내부 구현(Composable 함수가 컴파일 단계에서 IR과정을 거쳐 컴포즈 함수로 변환되는 과정과 이를 토대로 NodeTree를 구성하고 플랫폼별 Layout, Render(Drawing) 과정을 구현한 내용을 보면 놀랍다. 추후 하나씩 정리해보도록하자.
Layout?
Composition과정을 거쳐 생성되는 ElementTree(이하 Tree)의 measuring 과정이며 Tree의 값에따라 measuring skip을 구현하여 최적화를 지원한다.
간단하게 Layout이 진행되는 과정을 정리하면 아래와같다.
1
2
3
has Child
then Child.mesaure
else size -> place
Sooooo simple, 자식이 존재하면 재귀적으로 동작한다고 이해하면 쉬우며 최상위(root) node부터 최하위 노드까지 measure함수가 호출되며 최하위 노드의 size(크기)와 place(위치)를 통해 각 node 별 Coordinate값이 결정된다. (실제 구현이 recursive는 아니다)
즉, 자식 노드의 coordinate값이 먼저계산되고 이를 토대로 부모 노드의 coordinate값이 계산되는 방식이다. 해당 과정을 적절하게 커스텀하여 원하는 Layout을 얼마든지 쉽게 구현할 수 있으며 ConstraintLayout등과 같은 Layout은 불필요하다.
Custom Layout - ComposedBox
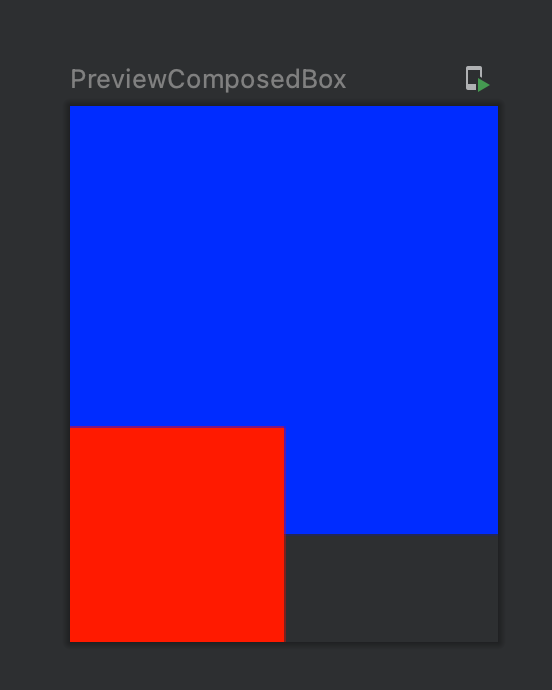
위와같은 UI 구현이 필요할때, Layout을 활용해보자.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
@Composable
fun ComposedBox(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
bottomContent: @Composable () -> Unit,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
Layout(
modifier = modifier,
content = {
content()
bottomContent()
})
{ measurable, constraints ->
val box = measurable[0].measure(constraints)
val bottom = measurable[1].measure(constraints)
layout(width = box.width, height = box.height + bottom.height / 2) {
box.placeRelative(0, 0)
bottom.placeRelative(0, box.height - bottom.height / 2)
}
}
}
@Preview
@Composable
private fun PreviewComposedBox() {
ComposedBox(
bottomContent = {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(50.dp)
.background(Color.Red)
)
},
content = {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.background(Color.Blue)
)
}
)
}
간단한 구현이며, content와 bottomContent를 받아 예시형태로 배치한다.
content가 2개뿐이라 measurable의 index로 접근했지만 아래처럼 layoutId 값을 기준으로 measurable 을 획득 할 수 있다.
1
measurable.find{ it.layoutId== "id"}?.let{ }
결론
이를 활용하면 Compose ContraintLayout의 활용없이 손쉽게 원하는 배치의 UI를 구현 할 수 있으니 참고하자.